|
Violet will be a good color for hair at just about the same time that brunette becomes a good color for flowers Fran Lebowitz |
Return back your hair with hair transplantation
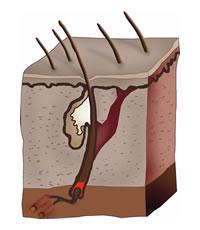
Types of hair lossThe healthy condition of the hair depends, to a very large extent, on the intake of sufficient amounts of essential nutrients in the daily diet. Hair is made of keratin, a protein, which also makes up the nails and the outer layer of our skin. One of the primary cause of hair loss is a high amount of the male hormone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) within the hair follicle. DHT is produced from testosterone in the prostate, various adrenal glands, and the scalp. After a period of time, an over abundance of DHT causes the hair follicle to degrade and shortens the active phase of the hair. Another factor that has been linked to hair loss is the amount of sebum in the scalp. Sebum contains a high amount of DHT, and clogs pores in the scalp, both of which cause the malnutrition of the hair root. The amount of sebum in balding hair is related to the amount of oil in the hair. Meanwhile most doctors agree that frequent shampooing is advised in hair loss cases with oily scalps. Another important cause of falling hair is stress, such as worry, anxiety and sudden shock. Stress leads to a severe tension in the skin of the scalp. This adversely affects the supply of essential nutrition required for the healthy growth of hair. Silicon bags are inserted beneath an area of hairy scalp and gradually inflated with saline water over a six-week period. This causes the hair-bearing skin to stretch, thus increasing the amount of hair-bearing scalp. After removing the bags, expanded hair bearing skin is lifted and moved to an adjacent bald area where a similar sized patch of scalp has been excised. For men, hair loss is male pattern baldness. Yes, there are other types of hair loss, including rare conditions such as alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis, where the entire scalp and entire body, respectively, become completely bald due to a viral condition that is irreversible. There is also patch baldness, in which hair falls out in patches of the scalp. This is caused by stress or poor nutrition or adverse scalp conditions. But the hair will usually grow back once the cause has been rectified. The effectiveness of medications used to treat alopecia depends on the cause of hair loss, extent of the loss and individual response. Generally, treatment is less effective for more extensive cases of hair loss. Finasteride is not approved for use by women. In fact, it poses significant danger to women of childbearing age. If you're a pregnant woman, don't even handle crushed or broken finasteride tablets because absorption of the drug may cause serious birth defects in male fetuses. Hair transplantation apply for women too!Hair transplantation has come a long way from the days of "hair plugs" and a pleasing, natural result is now routine. It is an excellent option for treatment of hereditary hair loss in many men and women. Hair transplantation refers to the surgical movement of permanent hair with its roots to an area of bald or balding skin. Hair transplantation is an effective and permanent solution for hair loss. Hair transplantation is done under local anesthesia as an outpatient procedure. Hair and follicles are removed from the "donor area" of permanent hair along the back and sides of the head. This area is immediately camouflaged by the surrounding hair. Most people require more than one session, each spaced at least six months apart each to complete the hair restoration in an area. The timing and number of transplants depends on the amount of hair you have when you start, how much is anticipated that you will continue to lose without transplanting and how much hair density you desire. In the hands of well-trained and experienced physicians, and using newer techniques with smaller grafts, the hair grows in the proper direction with a feathered hairline, and a highly aesthetic result. The hair is your own, and just like all of your hair it grows, can be washed, curled, cleaned, permed and styled as desired. Once the transplants are completed, no special maintenance is required. Hair transplantation is a cost-competitive solution for hair loss. Other hair replacement alternatives require additional maintenance over the years. The cost depends on the amount of bald area that will need to be transplanted, and the desired thickness. More grafts are necessary to cover more bald or thin area and to maximize hair density. Because the procedure is individual, costs are usually determined individually. Hair transplantation is universally accepted as a treatment for hair loss. While it was developed and first offered as a hair-loss treatment for men, women have increasingly found hair transplantation a viable option to correct the cosmetic deficit of thinning hair. Advances in hair transplantation techniques and better understanding of the biology of female hair loss contributed to the evolution of hair transplantation got women. Whether hair transplantation is a viable option for a woman with mild to moderate hair loss is a question to be answered by close consultation between the woman and the physician hair restoration specialist. Into that determination will go the patient's medical history, hair loss history, family medical and hair loss history, physical examination, scalp examination and laboratory tests as indicated by other examination results. How does hair grow?The outer layer is called the cuticle and is thin and colorless, its job is to protect the thicker cortex which contains the melanin. Melanin is responsible for the color of your hair and the actual color depends on what kind of melanin you have . The innermost layer of hair is called the medulla and reflects light giving hair the various color tones it has. That's why hair color looks a lot different in sunlight than it does in the shade. The physical thickness and length of hair depends on what type of hair it is. Vellus hair is the fine fuzz type of hair that's often called peach fuzz. Its very fine and colorless and often almost invisible to the naked eye. Conditions that can cause hair lossHair loss and thinning hair can be brought on by a variety of different conditions. Although, many researchers still pin most of the blame on genetics. The most common type of hair loss is referred to as "pattern hair loss" (androgenic alopecia). Many natural hair loss treatments exist that can help deal with pattern hair loss. Listed below are other conditions which can cause hair loss and thinning hair. Do you feel that you are the only one losing hair? You're not! The most common form of hair loss, Androgentic Alopecia, or pattern baldness, is experiences by 50-80% of Caucasian men. The number of Chinese males affected are half of the Caucasian counterparts while African Americans have a lower incidence of the condition as well. For women androgenetic alopecia occurs between 20-40% of the general female population. In summary, it is safe to say that pattern baldness is experienced by the norm of the population, you're not alone, but actually in the majority. Alopecia Areata - In this type of hair loss, hair usually falls out, resulting in totally smooth, round patches about the size of a coin or larger. It can, rarely, result in complete loss of scalp and body hair. This disease may affect children or adults of any age. The cause of alopecia areata is unknown. Apart from the hair loss, affected persons are generally in excellent health. In most cases, the hair regrows by itself. Dermatologists can treat many people with this condition. Treatments include topical medications, a special kind of light treatment, or in some cases pills. Medications - Some prescription drugs may cause temporary hair shedding. Examples include some of the medicines used for the following: gout, arthritis, depression, heart problems, high blood pressure, or blood thinner. High doses of vitamin A may also cause hair shedding. Cancer Treatments - Some cancer treatments will cause hair cells to stop dividing. Hairs become thin and break off as they exit the scalp. This occurs one to three weeks after the treatment. Patients can lose up to 90 percent of their scalp hair. The hair will regrow after treatment ends. Patients may want to get wigs before treatment. Major Surgery/Chronic Illness - Anyone who has a major operation may notice increased hair shedding within one to three months afterwards. The condition reverses itself within a few months but people who have a severe chronic illness may shed hair indefinitely. Physical and emotional stress might cause hair loss since body is recuperating from an overwhelming turmoil and simply shuts down hair production, thinking that it is not necessary for the body's survival, thereby contributing all energy toward repairing vital body parts. there can be up to three months delay between the major incidence and the actual hair loss. Moreover, there is also period of three months before the loss hair is replaced. This then means there is a total of a minimal of 6 moths for the total hair loss and regrowth cycle. Of course there are things that might contribute to hair loss such as anemia, low blood count, and thyroid abnormalities.
Definition interpretingScalp Czech dental clinic open for you
|